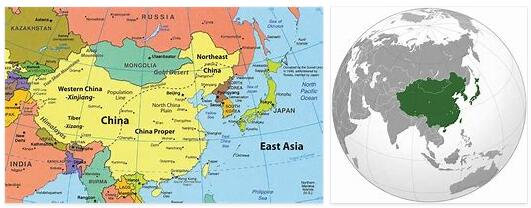
East Asia is the geographical area that is climatically determined by the non-tropical monsoon rains.
According to Countryaah.com, the region of East Asia includes the following nations:
- JAPAN
- CHINA
- MONGOLIA
- NORTH KOREA
- RUSSIA (North Amur area only)
- SOUTH KOREA
- TAIWAN
Japan
Japan is a country in East Asia. It consists of an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Korean Peninsula. The name is often translated as “Land of the Rising Sun”, comes from China, and refers to Japan’s eastern position in relation to the Asian continent. Before Japan had relations with China, it was known as Yamato (大 和). Wa (倭) was a name early China used to refer to Japan in “the period of the three kingdoms”.
Japan consists of a chain of islands. The largest of them are, counted from south to north: Kyushu (九州), Shikoku (四 国), Honshu (本州, the largest island) and Hokkaido (北海道).
The first census in Japan’s history took place in 1920. The census then showed 56 million residents. In 2000, the number was 126,925,843.
TIMELINE:
1638 – Japan expels foreigners and closes the country.
1945 – April 14. The Imperial Palace in Tokyo is being bombed by American planes.
1995 – March 20. A Japanese religious sect, Aum Shinri, detonates nerve gas bombs in Tokyo’s subway trains. 12 perish and more than 5,500 are hospitalized.
2007 – January 9. For the first time since World War II, Japan gets an actual Ministry of Defense. Since 1954, a defense office has handled the tasks. The office has kept a low profile due to Japan’s constitution and public opposition to memories of wartime militarism.
Mongolia
Mongolia is an independent inland state located in East and Central Asia. The country borders Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Mongolia has a land area of 1,594,116 km² and is thus the world’s 19th largest state in terms of area. With a population of about 2.8 million, Mongolia also has the lowest population density in the world among the independent nations. Ulan Bator, which in 2013 has approximately 1.3 million residents, is the country’s capital and largest city. Mongolia is a parliamentary republic.
Mongolia is today a parliamentary republic. In addition to being the world’s nineteenth largest state, Mongolia is also the world’s second largest inland state after Kazakhstan. The land consists of a modestly cultivated area as well as for the most part of steppe areas bordered by the Gobi Desert in the south and mountain areas in the north and west. About 30% of the country’s three million residents are nomadic or semi-nomadic. The dominant religion is Tibetan Buddhism, and the majority of the country’s population is of Mongolian ethnicity, supplemented by smaller groups of Kazakhs, Tuvans. and other peoples, primarily in the west of the country. About 20% of the population lives on less than $ 1.25 a day.
TIMELINE:
1206 – The Mongol Empire becomes the center of the country when it is established by Genghis Khan.
1279-1294 – Genghis Khan’s grandson Kublai Khan, founder of the Mongol Empire (1260-1294), became the founder and emperor of the Chinese Yang Dynasty. The empire was the largest contiguous empire in world history and stretched at its highest over an area of 35 million km² and included more than 100 million people.
1368 – After the collapse of the Yuan Dynasty, the Mongols retreat to what is now Mongolia.
16th-1700s – Mongolia came under the influence of Tibetan Buddhism. By the end of the 17th century, most of the land had been conquered and incorporated into the Qing Dynasty.
1912 – After the collapse of the Qing Dynasty, Mongolia declares independence, but the country struggled to establish an independent government and did not become independent until almost a decade later in 1921. During this period, the country came under strong Russian and Soviet influence.
1924 – The People’s Republic of Mongolia is established as a Soviet satellite state.
1990 – After the many revolutions in Eastern Europe in the autumn of 1989, Mongolia underwent its own revolution in 1990, which led to the fall of the Communist regime and the establishment of a new constitution in 1992, as well as the transition to a market economy.
Mongolia WTO and in recent years seeks to expand its trade relations, especially at regional level.
Democratic People’s Republic of Korea
North Korea, or officially the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, is the northern half of the Korean Peninsula in East Asia. North Korea borders South Korea to the south and China and Russia to the north.
TIMELINE:
1940s – Japan participated as one of the Axis powers in World War II, but by the end of the war, the Soviet Union managed to invade North Korea, while the United States invaded South Korea. The temporary boundary between the two occupation areas was at the 38th parallel.
2011 – December 17. Kim Jong-il died of a heart attack, at the age of 69; He had been in power since his father, Kim Il-sung’s death in 1994, after ruling since 1948. Kim Jong-il is succeeded by his son Kim Jong-un (born 1984), who is called the Great Successor.
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China is a state in East Asia. The name Republic of China is due to the fact that the government of Taiwan originated in mainland China, where from 1912 to 1949 it controlled large parts of China. Today, it controls only the island of Taiwan, which makes up 99% of the state’s area, as well as Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu and other small islands. Among the neighboring states are China, Japan and the Philippines. Taipei is the capital and Taiwan’s economic and cultural center while New Taipei City is the largest city in terms of population.
The oldest signs that humans have lived are about 20,000 – 30,000 years old. About 5,000 years ago, it is believed that farmers from mainland China came to settle. These people are believed to have spoken an Austronesian language, which is a language unrelated to Chinese. Taiwan’s indigenous peoples, who make up 2% of Taiwan’s population and speak Austronesian languages, are believed to be their descendants.
TIMELINE:
17th century – The Dutch colonized Taiwan, followed by a stream of Han Chinese and Hakkas from the Chinese territories: Fujian and Guangdong. Spain had for a short time a colony at the northern end of Taiwan but was driven out by the Dutch in 1642.
1945 – As a result of the end of World War II, the Republic of China gained control of Taiwan through the Kuomintang.
1949 – When the Republic of China loses the Civil War in China, it chooses to move it all to Taiwan and Kuomintang leader Chiang Kai-shek imposes a state of emergency.
1952 – Japan formally relinquishes all claims on Taiwan territory.