The very complicated relief and the humid and rainy climate of the town made the opening of roads, their maintenance and viability very difficult at all times. However, for a long time in history, the construction of communication routes is remembered. In 549 a. C., under the Emperor Suisei, tradition records the construction of some roads in Chūgoku; later, in 158 d. C., reigning the Emperor Kinmei, the great artery…
Read MoreJapan Religions Part II
Amidism was not until now officially represented in the country, although its doctrines had been more or less known, and even covered, by some of these reformers in their propaganda. Indeed, it seems that the statue sent by the king of Kudara to Japan in 552, the year that marks the introduction of Buddhism in the country, was precisely an image of Amida. The first Amidist sect appeared around 1000,…
Read MoreJapan Religions Part I
The constitution guarantees freedom of faith to all citizens, as long as this does not prejudice the maintenance of peace and public order or prevent the faithful from observing the laws. In addition to the ancient national religion, Shintoism, there are Buddhism, Confucianism and Christianity in Japan. The Shinto (v.) (From shin, god and t ō, street, doctrine) is, substantially, a mixed worship of nature and ancestors. It possesses divinity of the wind, of…
Read MoreJapan Mountains Part II
At S. dei M. Hida, a mountainous territory rich in vegetation begins, consisting of granite rocks on which the intensity of erosion is visible, rarely higher than 1000 m. In height: it is the M. Chūgoku chain that crosses the peninsula of the same name and seems to continue in Kyūshū in the chain of M. Tsukushi, more varied in geological formations. To the south-east of Hondo, under the Alpine…
Read MoreJapan Mountains Part I
Geologically, the islands of the Japanese archipelago represent nothing more than the highest portions of a vast mountain system facing the eastern coasts of the Asian continent, from which the intermediate depressions are detached from the seas occupying the depressions. In the Japanese stratigraphic series, all known systems are more or less completely represented, with the exception of the Archean. The oldest known formations still today belong to the Paleozoic,…
Read MoreJapan Literature Part III
A new phenomenon, which links literature even more to the development of information technologies, is that of keitai shōsetsu (novels on the mobile phone), productions of short narrative texts that are born with the 400-500 characters of a mobile phone screen and, through dedicated Internet sites, they reach a wide diffusion. They are mainly composed of girls between the ages of 15 and 25 who use pseudonyms to be able to freely…
Read MoreJapan Literature Part II
With the end of the war in 1945 and the regained freedom, there was an immediate revival of literary activities. Tendencies and ideas that had previously inspired the Japanese literary world reappear, which resumed with the international one the contacts interrupted during the conflict; periodicals that have already been suspended or suppressed come out again, others appear; they begin to write and publish authors who had already reached artistic maturity,…
Read MoreJapan Literature Part I
Around the beginning of the last fifty years, new currents begin to appear in the Japanese literary world and others already present are affirmed. Their common feature is a narrative aimed at objective reality, as opposed to the novel in the first person (Ich – roman, in Japanese watakushi sh ō setsu) which had already enjoyed undisputed domination. Among the most important is the Shinkankakuha (School of the new sense), in which the word meaning it indicates,…
Read MoreJapan Literature – The Renaissance under Tokugawa Part III
Apart from the censorship, the novel of manners had not been able to assert itself in Yedo, both because the intellectual element prevailed here, among which the tradition of good literature was alive and therefore lacked a taste for the obscene, and also because it he found himself competing with other genres that ended up taking over. First, among these, the jitsurokumono “authentic relations”, a kind of historical paraphrase, in…
Read MoreJapan Literature – The Renaissance under Tokugawa Part II
The Kannakusha, in their exaggerated admiration for Chinese things, went too far. Some even went so far as to give themselves a Chinese name, ashamed of having a Japanese one. The reaction could not fail and was nurtured by men who, for the fruitfulness of their writings and thought activities, had nothing to envy to their adversaries. The movement begins with a series of researches on ancient literature and then…
Read MoreJapan Literature – The Renaissance under Tokugawa Part I
The peace and prosperity established in the country by the Tokugawa created favorable conditions for the development of thought and studies. First, Ieyasu gave them the impetus. After his retirement (1605), he had many works collected and printed, founded libraries and a university, and surrounded himself with scholars who later held official positions. An essential feature of the time is that letters are democratized. The spread of education, mainly carried…
Read MoreLandmarks in Indonesia
Go on a study trip through Indonesia, the largest island nation in the world! Tourism is an important source of income for the country. Attractions such as Bali, the world heritage site Borobudur, Prambanan and various seaside resorts such as Pangandaran or other cultural places such as Bandung and Cirebon attract tourists from all over the world! Visit the most important cities of Indonesia, such as the capital Jabotabek (Jakarta)…
Read MoreGeorgia Landmarks
Jvari Monastery The Jvari Monastery is a sight in Georgia, near the former capital Mtskheta. It is one of the most historically important buildings in the country and is well worth a visit. It has been part of the UNESCO World Heritage List since 1996. Starting point of the Christianization of Georgia Today’s Jvari Monastery stands on the spot where St. Nino is said to have placed the first cross…
Read MoreAttractions in Borneo, Malaysia
Borneo, located in the Indonesian archipelago, is the third largest island in the world – with almost 5,000 km of coastline, most of which are relatively inaccessible due to mangrove swamps and where there are only a few bays. The real scenic attraction of Borneo is its dense jungle… with an incredibly colorful and lively nature, which has a lot to see in both flora and fauna. There are over…
Read MoreSightseeing in Bali, Indonesia
Of the Indonesian islands, Bali is probably the best known… a very popular one as well, and a seething one as well, because three quarters of the entire area is covered by mountains of volcanic origin. The highest volcano among them at 3,031 m is the Gunung Agung, in which the Balinese see the seat of the gods. At its feet there are important religious sights – these are places…
Read MoreArmenia Monastery
Geghard monastery The Geghard Monastery, which was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2000, is an important sight in the country Armenia, which is closely linked to the Christian faith. Anyone who is on study trips through the country should definitely visit the monastery. Geghard Monastery is located 35 kilometers east of the capital Yerevan in the upper Azattal. History The founding of the monastery, which dates back…
Read MoreIndia Literature
VEDIC LITERATURE The literary languages of India are only twelve, four of the Dravidian family (Deccan, southern India, northern Ceylon) and the others of the Indo-European family of the Indo-Aryan group (central and northern India, Pakistan). While ancient Vedic and Sanskrit literature crystallizes in the classicism of their respective languages, the Prakrites (vulgar languages), literally used in Jain and Buddhist dramas and religious texts, undergo a long process of evolution…
Read MoreIndia Arts: the Gupta and Post Gupta Age
The school of Mathura has the function of guide in the subsequent Gupta production, where the aesthetic and iconographic canons of Indian art are fixed. It is now established that the most “classic” sculptures of this school date back to the lower period (second half of the 5th century). Commonly considered Gupta production, actually to be attributed to the post-Gupta era, it is the later group of the Ajanta caves,…
Read MoreBahrain Geography and Economy
Bahrain – officially the Kingdom of Bahrain – is a country in the Middle East. It is one of the smallest in the region and is made up of five islands, of which the largest is the island of Bahrain, with 33 smaller islands. It is located in the Persian Gulf, sharing maritime borders with Qatar to the south and east; and with Saudi Arabia to the West and Northwest. According to Countryaah, Bahrain has 1.5 million residents. The Arabic word bahrain translated means ‘the kingdom…
Read MoreBangladesh Geography and Economy
Bangladesh, Officially called the People’s Republic of Bangladesh, is a country located in South Asia. Its territory is almost completely surrounded by India, except for a small strip to the southeast where it borders Myanmar. Geographically, the country is situated on the fertile ground of the Ganges Delta, which is why it is subject to annual floods caused by monsoons and cyclones. Together with the Indian province of West Bengal, it constitutes the…
Read MoreBhutan State Overview
Geography Although the Kula Kangri (7,544 m) was typically considered the highest mountain in the country. Subsequent topographic studies have concluded that the summit is entirely in China. According to these the highest peak would be the Gankhar Puensum at 7,540 m. Other distinctive mountains are the Black Mountains in the center of the country from 1,500 to 2,700 m. In the south we have the Silawik hills that reach…
Read MoreEast Timor Politics, Geography and Economy
Politics In August 2001, a popular consultation was convened again. More than 91% of the voters turned out to vote, this time to elect the members of a Constituent Assembly that was to write a new Constitution and establish the framework for the elections that would lead to total independence. Finally, the first Constitution was signed on March 22, 2002, and presidential elections were held on April 14. On May 20, Xanana Gusmao was elected President…
Read MoreKuwait City Overview
Kuwait. It is the capital city of the State of Kuwait, and has a 300-year history. The city has been rebuilt after the Gulf War. History The Emirate of Kuwait was founded in 1756 by Emir Sabah Habua Abdullah. In 1915 he accepted British protection. In 1961 he gained independence, and two years later he became a member of the United Nations. The political life of the emirate is characterized by the absolutism of the Emir, who, however,…
Read MoreMaldives Culture and Demography
Maldives are made up of around 1900 islands grouped into 26 atolls. They are located in the southwest of India, in the middle of the Indian Ocean. Most of the islands are small (around 40 hectares) and have a maximum level of a couple of meters above the sea. Less than 20% of the Maldives islands are inhabited, and of these only about 70 by indigenous population. Most of this population (about 300,000 residents)…
Read MoreOman Geography, Population and Economy
Geography Relief The region of Muscat, in the northeast, dominated by the Al Hajar Mountains, parallel to the Gulf of Oman, is the most differentiated area of the country. The Gulf of Oman, the northwestern arm of the Arabian Sea, stretches from the end of Hormuz to the Persian Gulf. One of its mountain ranges (Ajdar) has peaks that exceed 3,000 m in altitude. An arid plain, which occupies three-quarters…
Read MoreQatar Geography, Population and Economy
Geography Relief The relief is not very rugged. The center-east of the country is occupied by a limestone plateau, while the west coast has several hills of about 40 m of altitude. The northeast is a region of cliffs. The south is very dry and is dominated by dunes and shifting sands. In general, the soil is stony, with dune deserts and arid plains. Of the many coral islands that belong to Qatar, the…
Read MoreGeography of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
When the oil began to flow, according to Countryaah, the city of Abu Dhabi had just 46,000 people, four doctors, and five schools. Rich people had houses in the mud; the poorest families built their houses with reeds. That has been 50 years, when in 1958 British explorers discovered that there was the fifth largest oil reserve in the world, and 90% of it was located just below Abu Dhabi. Today this city, Capital of the United Arab…
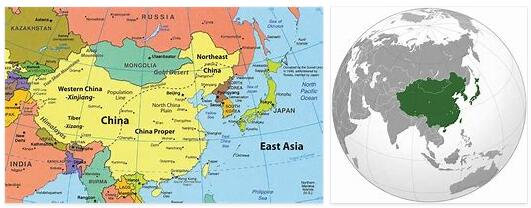
Read MoreEast Asia
East Asia is the geographical area that is climatically determined by the non-tropical monsoon rains. According to Countryaah.com, the region of East Asia includes the following nations: JAPAN CHINA MONGOLIA NORTH KOREA RUSSIA (North Amur area only) SOUTH KOREA TAIWAN Japan Japan is a country in East Asia. It consists of an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Korean Peninsula. The name is often translated as “Land of…
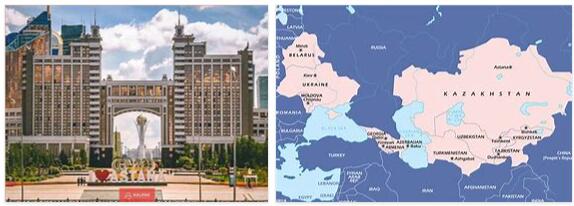
Read MoreCentral Asia
Central Asia is a region in Asia. There are different definitions of exactly what Central Asia includes. A delimitation which covers 9,029,000 km 2 or 21% of Asia’s area, says: KAZAKHSTAN (Asian part) CHINA (Qinghai and Xinjiang provinces) KYRGYZSTAN MONGOLIA TAJIKISTAN TIBET (part of China according to the UN) TURKMENISTAN UZBEKISTAN Another delimitation (used by UNESCO) is: AFGHANISTAN (parts of) INDIA (parts of) IRAN (northeast) CHINA (westernmost parts and Xinjiang)…
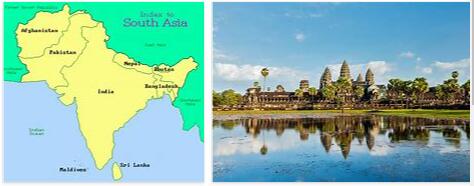
Read MoreSouth Asia
South Asia is a region in Asia that covers 4,480,000 km², which is 10 percent of Asia’s area. Parts of Afghanistan are sometimes included. The area is also called the Indian Subcontinent because it is located on its own continental plate separate from the rest of Asia. According to Countryaah.com, the region of South Asia includes the following nations: INDIA PAKISTAN BANGLADESH SRI LANKA BHUTAN MALDIVES Republic of India The…
Read More