Plant life in Jordan Plant growth is mostly of a dry Mediterranean type, with maquis scrub that has rich flowering in spring in the west, and goes into steppe and desert in the east. wormwood species as important elements. There is little forest. Wildlife in Jordan Ostrich, lion, cheetah, addax and oryx antelope were exterminated in Jordan in the early 1900s. Oryx has recently been reintroduced to the Shaumari Reserve.…
Read MoreTransportation in South America
Venezuela Venezuela has an exceptionally well-developed road network and is Latin America’s most impermeable country, largely due to the long, extremely low gasoline price. Paved roads, mainly Pan-American Highway, connect Venezuela with the rest of South America via Colombia. Rough terrain in the east combined with a border conflict means that there are no land links with Guyana. The rail network is almost non-existent and there is no train traffic…
Read MoreArt in Cambodia
Early art and artifacts from the Mekong Delta show the influence of Chinese Han culture, Iran and, above all, India, especially in representations of Hindu gods. Early Angkor style An example from this period (ca. 860-1000) is the temple of Prah Ko from 879. Ta Keo from around the year 1000 is a fully developed Khmer temple with a high central tower, surrounded by four lower tower buildings on a…
Read MoreFlags of Europe
Albania The flag is from 1913, the year after the country’s declaration of independence. The double eagle as a symbol of power in both the east and the west was the former Byzantine Empire’s coat of arms and dates back to the 1460’s and the freedom hero Skanderbeg, who used the symbol. From 1945–92 there was also a Soviet star (in yellow outlines) on the flag cloth above the double…
Read MoreRussia Arts and Literature
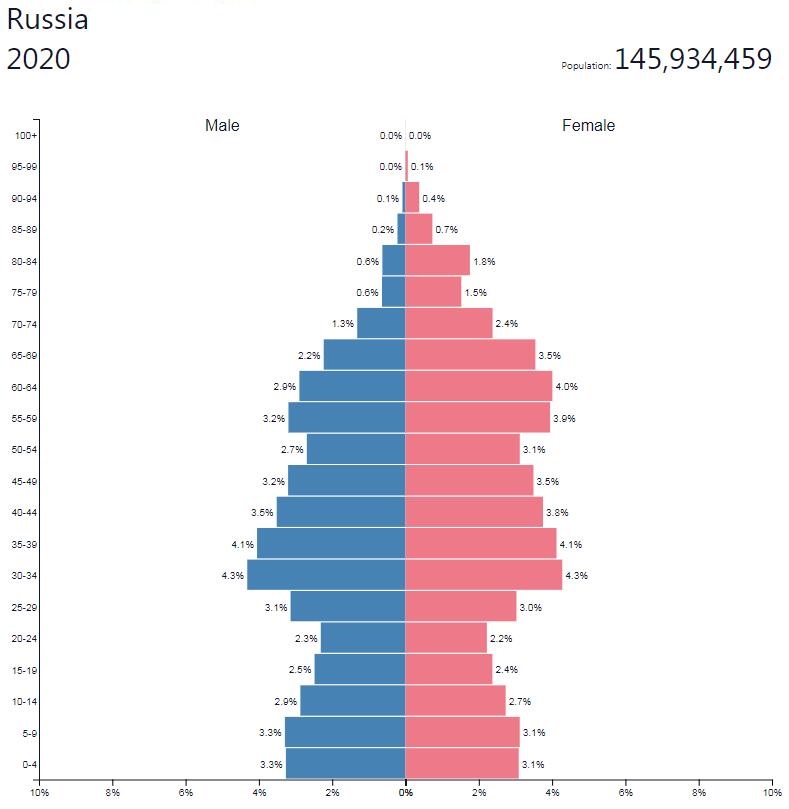
Literature Characteristic of the literature in Russia has been its close connection with the development of society. Where religious preaching has been weak and no political layer has ever really developed, the authors have instead taken the role of outlining the direction of the future. The authorship with its unification of life and works has thus gained an extremely special significance. However, it was not until the 19th century that…
Read MoreChina Arts and Literature
Literature Confucianism’s emphasis on the didactic function of literature has led to the boundary between enlightenment literature and fiction of old being vague. As far more important is the boundary between the culture-promoting literature and the vulgar literature that did not meet the requirements set for “true” literature in terms of subject matter or form. The withering literature is written in a script (Wenyan), which is strongly different from the…
Read MoreIndia Arts and Literature
Literature The oldest literary history of the Indo-languages is divided into a Vedic period and a classical Sanskrit period. Towards the end of the first millennium AD got Sanskrit competition of the Middle Indian languages. About 1000 AD began to develop the distinctive literature, and it was richly represented from the 15th century in many modern Indian languages. Other language groups in the Indian environment have produced literature, e.g. nevari.…
Read MoreAzerbaijan Arts and Literature
Literature In Azerbaijan there is a rich oral tradition of folk songs and heroic epics that were developed long before the entry of Islamic culture into the area. Since the 17th century, a native variant of the poem “Köroǵlu”, widely distributed in the Orient, has existed, praising the unrighteous ruler figure. Among the highlights of medieval literature are Nezami’s Persian written poems “Treasury of Secrets” and “Lejli and Medzjun”, both…
Read MoreArmenia Arts and Literature
Film During the First World War, Armenian photographers in journal films depicted the fighting between Russians and Turks on the Caucasian front. The first Armenian feature film is considered A. Minervin’s “Under the Kurds” (1915). After the brief independence, the film was nationalized in 1923 under the direction of a.k.a. director Amo Bek-Nazarov, who for a long time had a central position in Armenian film life. In addition to journal…
Read MoreAfghanistan Arts and Literature
Literature Afghanistan’s literature is written in several languages. Much of the classical literature in Persian (dari) was created in what is now Afghanistan; compare Iran (literature). From the 18th century, the literature in Afghanistan developed more in connection with the Persian poetry in India than in Iran. Poetry remained traditional for a long time, and first with poets such as Golpacha Olfat (1909-77) and Khalilollah Khalili (1909-87) contemporary themes were…
Read MoreGeorgia Arts and Literature
Literature In addition to a rich, oral vernacular, in Georgia early church literature was developed under Byzantine influence; the oldest manuscript is from 864. The advent of a Georgian nation state in the early 12th century brought a cultural boost. During Queen Tamar’s reign (1184-1212), court poetry and the knight novel flourished, and Sjota Rustaveli wrote his heroic poem “The Knight in the Tiger Traps” (not in Swedish translation) which…
Read MorePhilippines Arts and Literature
Literature The oldest history of Philippine literature is characterized by the linguistic diversity that once separated the people of the different islands. Prior to the Spanish conquest, literature consisted mainly of poetry, which was recited or sung. The most popular forms were kundiman (love songs), kumentang (oden) and awit (ballads). Of this older literature, only fragments remain today, as it was rarely recorded on the native alphabet. Countryaah: Population and…
Read MoreBurma Arts and Literature
Literature Burma’s literature has ancient origins and is extensive but so far unexplored. The earliest documents (400-500) are written in Pali and reproduce sections from the Buddhist canon. Stone inscriptions have been preserved from the Pagan dynasty (1044-1287), which marks the very beginning of Burmese literature, while the early palm leaf texts have been completely lost. The authors – usually members of the royal house, high-ranking officials or Buddhist monks…
Read MoreIndonesia Arts and Literature
Literature The older literature, both oral and written, is characterized by regional diversity. In particular, the Javanese tradition of stories with motifs from the Indian epic Mahabharata and Ramayana, which also characterized the shadow play wayang, can be mentioned. In addition, there are a rich Islamic theological literature. Indonesia’s modern literature was given the opportunity to develop when the common Indonesian language (bahasa indonesia) was adopted in 1928. However, the…
Read MoreIraq Arts and Literature
Literature, drama and theater Iraq had an early literary culture (see Assyria, Literature and Babylonia), Literature). Through the conquest of the Muslims, Basra and Kufa became centers, not only politically but also for Arab philology, Koran exegesis and literary science. During the Abbasid dynasty, the center of the Islamic empire, even in cultural terms, was shifted from Damascus to the new city of Baghdad. The Caliph al-Mamun was established in…
Read MoreIran Arts and Literature
Literature By Iranian literature in a broad sense is meant texts in the various Iranian languages during their more than 2,500-year history, in the narrower sense only literature in the currently dominant Iranian writing language, Nypersian (even Persian). Here, this Persian literature and its historical background are dealt with in Avestian, Ancient Persian and Middle Persian literature. Persian literature was created in the Iranian cultural sphere, which, in past historical…
Read MoreIsrael Arts and Literature
Literature The literature in Israel is primarily written in Hebrew or Yiddish. In Arabic, Palestinian fiction is also published, see Palestine (Literature). Compare also Jewish literature. Modern Hebrew literature was born in Europe during the late 18th century cultural enlightenment among the Jews (Hebrew haskala). In Palestine, Hebrew literature was developed at the end of the 19th century, since Eliezer Ben-Yehuda had revived the “tongues of the prophets” so that…
Read MoreJapan Arts and Literature
Coin Initially, the Japanese coin system developed completely outside of Western influence but was strongly influenced by the Chinese. The lowest denominations (in copper) look almost like the Chinese counterparts. They are round with square holes in the middle (cash) and were issued in the years 708-958 with a total of 12 types, which became easier. There were also some issues in gold (from 760) and silver. Countryaah: Population and…
Read MoreYemen Arts and Literature
Literature A very old tradition of poets who write both in classical Arabic and in the vernacular lives on in the country; there are also mixed forms with regard to grammatical structures and vocabulary. For example, the medieval verse form muwashshah used in Yemen in classical Arabic has become a form of poetry in the vernacular. This poetry has developed into both a medium for national and political messages as…
Read MoreJordan Arts and Literature
Literature After the British mandate over Jordan had been repealed, the national culture came to life again. In the field of literature, lyric has played the most important role, with new classics such as Muhammad Hasan Ala ad-Din or representatives of a formally freer lyric such as Haydar Mahmud. Radi Sadduq and the female poet Samira al-Khatib are among the strongest Israeli-critical poets, who in love symbols express their pain…
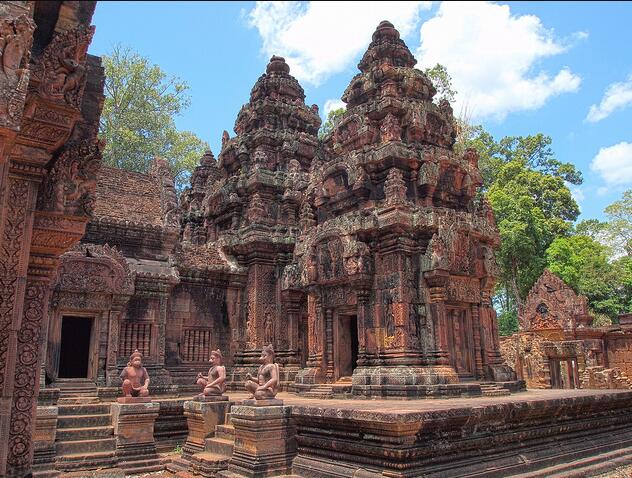
Read MoreCambodia Arts and Literature
Literature The time until 1600 In the oldest literature from Cambodia, Indian traditions in Sanskrit and Pali meet as well as indigenous traditions of Khmer. The literature consists mainly of Indian art poetry which praises the ruler, in the form of stone inscriptions that date back to the 4th century AD. From these inscriptions it appears that classical Indian works in Sanskrit were known. From 611 AD there are also…
Read MoreKazakhstan Arts and Literature
Literature Hero songs, fairy tales and legends are the origin of Kazakh literature. The motif of the song-cat was developed by the acynes, the bards, who seemed to speak orally in the villages and with the big men. In the poetry of Abaj Kunanbaev, the Akyn tradition was renewed in the 19th century. through his encounter with Russian literature and classical Western philosophy. Abaj also made many records of the…
Read MoreKyrgyzstan Arts and Literature
Literature Like other Central Asian literature, the Kyrgyz also has its roots in the poetry of acynes (folk songs) with its lamentations and didactic pieces. Here there is a rich treasure of fairy tales, legends and proverbs, but above all the great epic about the national hero Manas, comprising more than 500,000 rows (recorded in excerpts first in 1856). Notably, among the Kyrgyz acynes was Toktogul Satylganov, one of the…
Read MoreLaos Arts and Literature
Literature Lao’s oral poetry has its chief expression in phagna souphasite, short proverbs on rhyme, and in lamb, narrative ballad, the most popular form of poetry. The motifs in the latter often originate in jataka. Classic in the genre is “Sin Xay” by Thao Pangkham (18th century). From Ramayana was retrieved “Prince Lak and Prince Lam”, once the most staged drama. Popular literature consists of long lambs and has ingredients…
Read MoreLebanon Arts and Literature
Literature Contemporary literature is characterized mainly by classical Arabic-Islamic tradition (see Arabic literature), but also by the Eastern Churches and by the Western Missionary Movement from France and the United States. The cultural debate has been marked by the meeting between the Arab, Oriental world of thought and the Western rationalist and materialist tradition. As in the rest of the Arab world, poetry has maintained its culture-dominant position, although many…
Read MoreMalaysia Arts and Literature
Literature, drama and theater The area has a rich traditional folk poetry. In the classical literature there are both Hindu and Islamic elements. Among older texts, the historical 15th-century chronicle “Sejarah Melayu” deserves mention, as do numerous hikayat- stories or stories. The emergence of modern literature is linked to Abdullah bin Abdul Kadir Munshi, especially through his autobiography “Hikayat Abdullah” (1849). In addition to Malay, there are significant poems in…
Read MoreMongolia Arts and Literature
Literature The Mongolian literature owns an extensive treasure trove of oral traditions and tales. These include the big hero bag “Gesar” and “Djanggar”. The oldest written literary memorial is “The Secret History of the Mongols” (earliest 1240), which is the first in a long line of more or less literary chronicles, of which “Altan tobci” (1655) and “Erdeni-yin tobci” (1662) are the most famous. Countryaah: Population and demographics of Mongolia,…
Read MoreNepal Arts and Literature
Literature Nepal’s dominant literary language was in ancient times newari. The classical Newari literature mainly consisted of folk songs, historical chronicles, paraphrases and adaptations of storytelling literature from India as well as plays where a fusion between the classical Indian theater and a domestic lyrical singing tradition. During the Rana regime, the literary activity of newari came to be strongly suppressed, and only by the restoration of the constitutional monarchy…
Read MoreNorth Korea Arts and Literature
Film After the split of Korea at the end of World War II, Kim Il Sung declared in Lenin’s spirit the film as the most important of arts. In 1946, the Korean documentary film studio was created, in 1947 the Korean film studio for feature films in Pyonyang and in 1959 was added to the Korean army’s April 25 studio (originally called the February 8 studio). In the 1990’s, the…
Read MorePakistan Arts and Literature
Literature Pakistan has taken over a rich literary tradition in all its main languages, e.g. Urdu, Panjabi, Sindhi, Baluchi, Pashto, and English. For centuries, Urdu has been primarily the literary language of the Muslims in the Indian subcontinent. In his writing, Muhammad Iqbal has formulated the ideological basis for the formation of the state of Pakistan and thus further legitimized Urdu’s special status as the official language. At the same…
Read More